If you receive abnormal results from a cervical smear test, it is important that a gynaecologist examines your cervix in more detail. They are able to do so using a colposcope, which magnifies the cells of your cervix to make them more visible. However, you may sometimes need a colposcopy if you have unexplained bleeding, pelvic pain or an inflamed cervix. The procedure is painless and you will usually have the results of the test straight away, allowing your specialist to explain whether you need treatment.
► Routine screening picked up abnormal smear
► Bleeding after having sexual intercourse
► Unscheduled bleeding between periods
► Blood stained discharge per vagina
► If you have high risk human papilloma virus, even if your smear is normal.
 |
 |
|
|
Picture of a colposcope |
Not painful done by the doctor in the clinic |
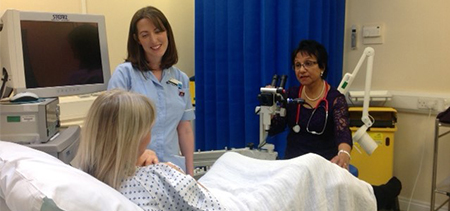
Dr Sheela performing colposcopy in her clinic
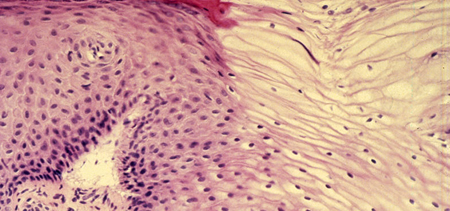
Around 1% of cervical smears shows moderate changes in your cells and a further 0.5% of smears show severe changes. If your smear test shows either of these or mild changes with a high risk of infection with HPV, the virus linked to cervical cancer, detailed examination of your cervix is recommended. This is also advised if three smear tests in a row are unable to provide enough information about possible changes within your cervical cells.
When arranging your colposcopy it is advisable that the appointment doesn't coincide with your period and you will also be given specific advice of anything to avoid in the 24 hours before your test. Before the procedure you will usually be asked about your periods, the contraception you use and your general health. During the examination itself a speculum is used to open your vagina to allow access to your cervix to provide a clear view, but the colposcope doesn't come into direct contact with your cervix. A liquid might be added to your cervix though to allow clearer identification of any abnormal cells. If any unusual cells are found, a biopsy removes tiny areas of your cervix to allow the lab to carry out further tests. However, if it is certain that abnormal cells are present, it is sometimes possible to receivetreatment of abnormal smear results at this appointment.
If a biopsy was taken, you will need to wait for the results of these before you can start treatment. The results indicate whether any cells with the potential to become cancerous were found and these are graded according to the proportion of cells in the sample that were affected. For instance, grade 1 is where up to one-third of cells are affected, grade 2 is where as many as two-thirds are abnormal and grade 3 is where all the cells are abnormal. Rarely, a biopsy may detect cancerous cells. Treatment is not always necessary with grade 1 cells, as around 60% of the time these normalise of their own accord, and you will simply need a repeat examination once or twice a year. However, with grade 2 and 3 cells, you will need treatment to remove them. On the rare occasions that cancer is found, you will receive a rapid referral to start suitable treatment.
If a biopsy confirms you have grade 2 or 3 cervical cells, your gynaecologist will discuss treatment using a procedure called loop excision. This procedure removes the area of abnormal cells from your cervix with a thin loop made of wire, which is heated using a current. It is possible to perform loop excision under local anaesthetic, which is delivered by an injection to your cervix. However, a general anaesthetic may be necessary if a larger area of your cervix is affected. It is normal to bleed slightly after a loop excision, which may last for several weeks afterwards. Sanitary towels rather than tampons should be used to manage your blood loss, as tampons are inadvisable for four weeks, as is intercourse to reduce the likelihood of infection. After treatment of abnormal smear tissue, a sample is sent for further investigation and a repeat colposcopy is recommended within six months of treatment. Dr Sheela Purkayastha will then decide whether further cervical examinations with a colposcope are required.
Although effective treatment is available when you receive an abnormal smear, it is best to avoid this situation if possible. As nearly all cases of abnormal cervical cells are attributable to HPV, practising safe sex is essential. However, you can greatly reduce your risk by having a cervical cancer vaccine before you become sexually active, which is why the vaccination is routinely offered to girls aged 12 and 13. If you missed out on this vaccine though, even women in their early and late twenties may benefit from the cervical cancer vaccine, so you may wish to discuss this with Dr Purkayastha.
To arrange an examination following an abnormal cervical smear, phone today to book your test.

![]() Privacy Policy | Disclaimer | Links | Sitemap | View Mobile Website
Privacy Policy | Disclaimer | Links | Sitemap | View Mobile Website
The contents on this site is for information only, and is not meant to substitute the advice of your own physician or other medical professional.